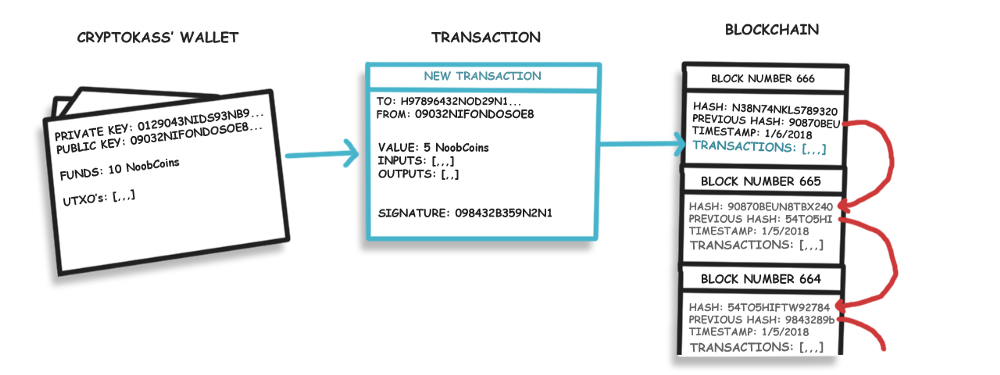
区块链是分布式数据存储、点对点传输、共识机制、加密算法等计算机技术的新型应用模式。所谓共识机制是区块链系统中实现不同节点之间建立信任、获取权益的数学算法 。
前言
本系列教程旨在帮助你了解如何开发区块链技术。【译】用Java创建你的第一个区块链-part2
本章目标
- 创建一个简单的钱包。
- 使用我们的区块链发送带签名的交易。
- 感觉很吊
这样我们就有自己的加密货币
值得注意的是,这里创建的区块链并不是功能完全的完全适合应用与生产的区块链,相反只是为了帮助你更好的理解区块链的概念。
别担心,这实际上是很简单的,但比上一个教程要长!
在上衣章节【译】用Java创建你的第一个区块链-part2,我们已经有了一个基本的区块链,但在区块链中存放的是一些无用的信息。今天我们将用交易取代这些信息(我们的区块将能够保存多个交易),允许我们创建一个非常简单的加密货币,我们的货币名字NoobCoin。
- 本教程是在上一边基础上实现的
- 导入 bounceycastle和
GSON
准备一个钱包
在加密货币中,在区块链作为交易时,货币所有权可以进行转移,每个参与者都有一个自己私有的地址来发送或者是收取货币。,钱包可以存储这些地址。因此钱包就是可以在区块链上进行新交易的软件。
Don’t worry about the information on the transaction, that will be explained soon
让我们创建一个钱包类来保存公钥和私钥:
package noobchain;
import java.security.*;
public class Wallet {
public PrivateKey privateKey;
public PublicKey publicKey;
}
公钥和私钥究竟是起到什么作用呢,其实公钥的作用就是地址,你可以分享你的公钥给别人以此来获取付款,而你的私钥的作用是为了对交易进行签名,这样其他人就不可以花费你的金额除非它拥有你的私钥,所以对于每个人而言我们必须保护好我们的私钥,不能透露我们的私钥信息给其他人。同时在我们进行交易的时候我们也会同时发送我们的公钥由此来验证我们的签名是有效的而且没有数据被篡改。
我们在密钥对KeyPair生成私有和公钥。我们将使用椭圆曲线加密来生成我们的密钥对KeyPair。让我们将generateKeyPair()方法添加到我们的钱包类中,并在构造函数中调用它:
私钥用于签署我们不想被篡改的数据。公钥用于验证签名。
package noobchain;
import java.security.*;
public class Wallet {
public PrivateKey privateKey;
public PublicKey publicKey;
public Wallet(){
generateKeyPair();
}
public void generateKeyPair() {
try {
KeyPairGenerator keyGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("ECDSA","BC");
SecureRandom random = SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG");
ECGenParameterSpec ecSpec = new ECGenParameterSpec("prime192v1");
// Initialize the key generator and generate a KeyPair
keyGen.initialize(ecSpec, random); //256 bytes provides an acceptable security level
KeyPair keyPair = keyGen.generateKeyPair();
// Set the public and private keys from the keyPair
privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
}catch(Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
你不需要完全理解椭圆曲线加密算法的核心逻辑究竟是什么,你只需要它是用来创建公钥和私钥,以及公钥和私钥分别所起到的作用是什么就可以了。
现在我们已经又了钱包类的大概框架,下面我们再来看一下交易类。
交易和数字签名
每笔交易将携带一定以下信息:
- 资金付款人的公匙信息。
- 资金收款人的公匙信息。
- 被转移资金的金额。
- 输入,它是对以前的交易的引用,证明发送者有资金发送。
- 输出,显示交易中收款方相关地址数量。(这些输出被引用为新交易的输入)
- 一个加密签名,证明该交易是由地址的发送者是发送的,并且数据没有被更改。(阻止第三方机构更改发送的数量)
让我们创建这个新的交易类:
import java.security.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Transaction {
public String transactionId; // this is also the hash of the transaction.
public PublicKey sender; // senders address/public key.
public PublicKey reciepient; // Recipients address/public key.
public float value;
public byte[] signature; // this is to prevent anybody else from spending funds in our wallet.
public ArrayList<TransactionInput> inputs = new ArrayList<TransactionInput>();
public ArrayList<TransactionOutput> outputs = new ArrayList<TransactionOutput>();
private static int sequence = 0; // a rough count of how many transactions have been generated.
// Constructor:
public Transaction(PublicKey from, PublicKey to, float value, ArrayList<TransactionInput> inputs) {
this.sender = from;
this.reciepient = to;
this.value = value;
this.inputs = inputs;
}
// This Calculates the transaction hash (which will be used as its Id)
private String calulateHash() {
sequence++; //increase the sequence to avoid 2 identical transactions having the same hash
return StringUtil.applySha256(
StringUtil.getStringFromKey(sender) +
StringUtil.getStringFromKey(reciepient) +
Float.toString(value) + sequence
);
}
}
我们还应该创建空的transactioninput和transactionoutput类,不要担心我们可以在后面填写它们。
我们的交易类还将包含生成/验证签名和验证交易的相关方法,那么签名的意图是什么?签名在我们的区块链中执行了两个非常重要的任务:第一,签名用来保证只有货币的拥有者才可以用来发送自己的货币,第二,签名用来阻止其他人试图篡改提交的交易。
即私钥被用来签名数据,而公钥用来验证其完整性。
举个例子:Bob 想要发送2个加密货币给Sally,他们用各自的钱包创建了交易,并提交到全网的区块链中作为一个新的区块,一个挖矿者试图篡改接受者把2个加密货币给John,但是幸运的事,Bob在交易数据中已经用私钥进行了签名,这就允许了全网中的任何节点使用小明的公匙进行验证数据是否已经被篡改(因为没有其他人的公钥可以用来验证小明发出的这笔交易)。
从前面的代码中我们可以看到我们的签名将是一堆字符串,所以让我们创建一个方法来生成它们。首先我们在StringUtil类中创建产生签名的方法。
public static byte[] applyECDSASig(PrivateKey privateKey, String input) {
Signature dsa;
byte[] output = new byte[0];
try {
dsa = Signature.getInstance("ECDSA", "BC");
dsa.initSign(privateKey);
byte[] strByte = input.getBytes();
dsa.update(strByte);
byte[] realSig = dsa.sign();
output = realSig;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return output;
}
//Verifies a String signature
public static boolean verifyECDSASig(PublicKey publicKey, String data, byte[] signature) {
try {
Signature ecdsaVerify = Signature.getInstance("ECDSA", "BC");
ecdsaVerify.initVerify(publicKey);
ecdsaVerify.update(data.getBytes());
return ecdsaVerify.verify(signature);
}catch(Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static String getStringFromKey(Key key) {
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(key.getEncoded());
}
不用担心你不能理解这些方法的内容,你所需要知道的就是
applyECDSASig方法的输入参数为付款人的私钥和需要加密的数据信息,签名后返回字节数组。而verifyECDSASig方法的输入参数为公钥、加密的数据和签名,调用该方法后返回true或false来说明签名是否是有效的。getStringFromKey返回任何key的编码字符串
让我们使用签名的方法在交易类中,增加generatesiganature() 和 varifiysignature()方法:
//Signs all the data we dont wish to be tampered with.
public void generateSignature(PrivateKey privateKey) {
String data = StringUtil.getStringFromKey(sender) + StringUtil.getStringFromKey(reciepient) + Float.toString(value) ;
signature = StringUtil.applyECDSASig(privateKey,data);
}
//Verifies the data we signed hasnt been tampered with
public boolean verifiySignature() {
String data = StringUtil.getStringFromKey(sender) + StringUtil.getStringFromKey(reciepient) + Float.toString(value) ;
return StringUtil.verifyECDSASig(sender, data, signature);
}
在现实中,您可能希望签名更多信息,例如使用的输出/输入和/或时间戳(现在我们只是签名最低限度的信息)
签名将由矿工验证,只有签名验证成功后交易才能被添加到区块中去。
当我们检查区块链的有效性时,我们也可以检查签名
测试钱包和签名
现在我们简单的进行一些测试,在主方法中,我们增加了一些新的变量也替换了我们之前在主方法中的一些内容。
import java.security.Security;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Base64;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
public class NoobChain {
public static ArrayList<Block> blockchain = new ArrayList<Block>();
public static int difficulty = 5;
public static Wallet walletA;
public static Wallet walletB;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Setup Bouncey castle as a Security Provider
Security.addProvider(new org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider());
//Create the new wallets
walletA = new Wallet();
walletB = new Wallet();
//Test public and private keys
System.out.println("Private and public keys:");
System.out.println(StringUtil.getStringFromKey(walletA.privateKey));
System.out.println(StringUtil.getStringFromKey(walletA.publicKey));
//Create a test transaction from WalletA to walletB
Transaction transaction = new Transaction(walletA.publicKey, walletB.publicKey, 5, null);
transaction.generateSignature(walletA.privateKey);
//Verify the signature works and verify it from the public key
System.out.println("Is signature verified");
System.out.println(transaction.verifiySignature());
}
确定要添加
bounceycastle依赖
我们创建了两个钱包walleta和walletb,然后打印了walleta的私钥和公钥。生成一个交易并使用walleta的私钥对其进行签名。
打印
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:55757', transport: 'socket'
Private and public keys:
MHsCAQAwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQEEYTBfAgEBBBiJzZiesBnBWwwB+uog+fJX84mx4lPUTUagCgYIKoZIzj0DAQGhNAMyAAQfPzad0zqBUGQAany2rRZE1+2ml5IOCZST8LywjBQT8ux+3UPVbr2u0+LaExxz1WI=
MEkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQEDMgAEHz82ndM6gVBkAGp8tq0WRNftppeSDgmUk/C8sIwUE/Lsft1D1W69rtPi2hMcc9Vi
Is signature verified
true
接下来我们将创建并验证输入和输出,并把交易保存到区块链中去。
输入和输出 1:如何验证货币是你的
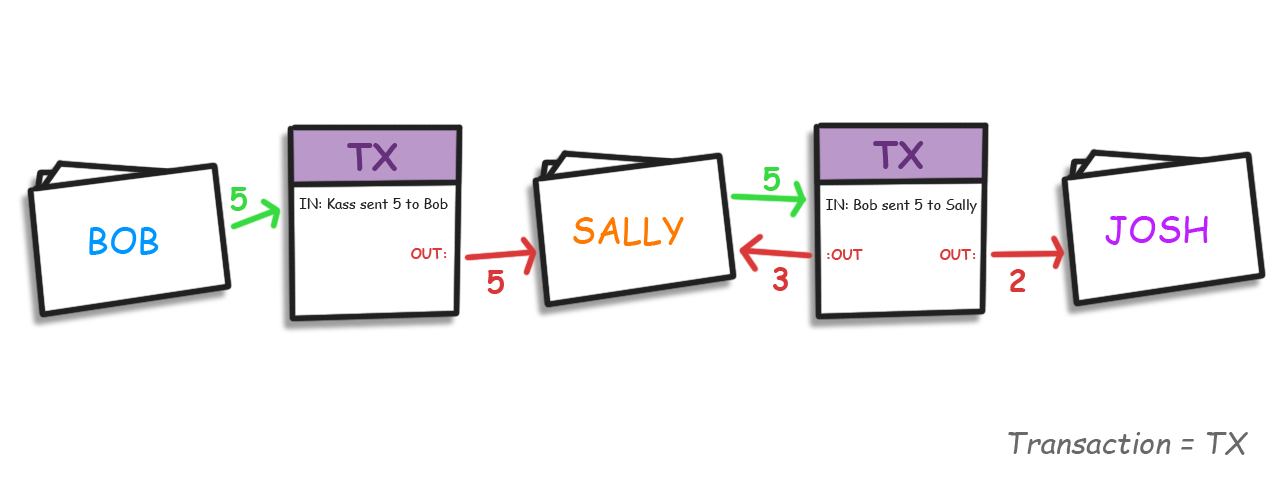
如果你拥有1比特币,你必须前面就得接收1比特币。比特币的账本不会在你的账户中增加一个比特币也不会从发送者那里减去一个比特币,发送者只能指向他/她之前收到过一个比特币,所以一个交易输出被创建用来显示一个比特币发送给你的地址(交易的输入指向前一个交易的输出)。
你的钱包余额是所有未使用的交易输出的总和
从这一个点出发,我们会依照比特币中的说明,把所有未使用的交易输出称为UTXO.
创建TransactionInput 类:
public class TransactionInput {
public String transactionOutputId; //Reference to TransactionOutputs -> transactionId
public TransactionOutput UTXO; //Contains the Unspent transaction output
public TransactionInput(String transactionOutputId) {
this.transactionOutputId = transactionOutputId;
}
}
这个类将用于引用尚未使用的
transactionoutput。transactionOutputId将用于查找相关的TransactionOutput,允许矿工检查您的所有权。
创建TransactionOutputs 类:
import java.security.PublicKey;
public class TransactionOutput {
public String id;
public PublicKey reciepient; //also known as the new owner of these coins.
public float value; //the amount of coins they own
public String parentTransactionId; //the id of the transaction this output was created in
//Constructor
public TransactionOutput(PublicKey reciepient, float value, String parentTransactionId) {
this.reciepient = reciepient;
this.value = value;
this.parentTransactionId = parentTransactionId;
this.id = StringUtil.applySha256(StringUtil.getStringFromKey(reciepient)+Float.toString(value)+parentTransactionId);
}
//Check if coin belongs to you
public boolean isMine(PublicKey publicKey) {
return (publicKey == reciepient);
}
}
交易输出类将显示从交易中发送给每一方的最终金额。这些作为新交易中的输入参考,作为证明你可以发送的金额数量。
输入和输出 2:处理交易
区块链可能会收到很多交易,而区块链可能会非常长,因为我们必须查找并检查其输入,所以可能需要非常长的时间来处理新的交易。为了解决这个问题,我们保存了一个额外的集合称之为为使用的交易作为可用的输入,所以在主函数中增加一个集合称为UTXO。
public class NoobChain {
public static ArrayList<Block> blockchain = new ArrayList<Block>();
public static HashMap<String,TransactionOutputs> UTXOs = new HashMap<String,TransactionOutputs>(); //list of all unspent transactions.
public static int difficulty = 5;
public static Wallet walletA;
public static Wallet walletB;
public static void main(String[] args) {
hashmap允许我们使用键来查找值,但是您需要导入java.util.hashmap
重点来了,我们在交易类中增加一个processTransaction方法,这个方法是把一切放在一起用来处理交易。
//Returns true if new transaction could be created.
public boolean processTransaction() {
if(verifiySignature() == false) {
System.out.println("#Transaction Signature failed to verify");
return false;
}
//gather transaction inputs (Make sure they are unspent):
for(TransactionInput i : inputs) {
i.UTXO = NoobChain.UTXOs.get(i.transactionOutputId);
}
//check if transaction is valid:
if(getInputsValue() < NoobChain.minimumTransaction) {
System.out.println("#Transaction Inputs to small: " + getInputsValue());
return false;
}
//generate transaction outputs:
float leftOver = getInputsValue() - value; //get value of inputs then the left over change:
transactionId = calulateHash();
outputs.add(new TransactionOutput( this.reciepient, value,transactionId)); //send value to recipient
outputs.add(new TransactionOutput( this.sender, leftOver,transactionId)); //send the left over 'change' back to sender
//add outputs to Unspent list
for(TransactionOutput o : outputs) {
NoobChain.UTXOs.put(o.id , o);
}
//remove transaction inputs from UTXO lists as spent:
for(TransactionInput i : inputs) {
if(i.UTXO == null) continue; //if Transaction can't be found skip it
NoobChain.UTXOs.remove(i.UTXO.id);
}
return true;
}
//returns sum of inputs(UTXOs) values
public float getInputsValue() {
float total = 0;
for(TransactionInput i : inputs) {
if(i.UTXO == null) continue; //if Transaction can't be found skip it
total += i.UTXO.value;
}
return total;
}
//returns sum of outputs:
public float getOutputsValue() {
float total = 0;
for(TransactionOutput o : outputs) {
total += o.value;
}
return total;
}
我们还添加了
getinputsvalue方法
通过这种方法,我们执行一些检查以确保交易有效,然后收集输入并生成输出。最重要的是,最后,我们抛弃了输入在我们的UTXO列表,这就意味着一个可以使用的交易输出必须之前一定是输入,所以输入的值必须被完全使用,所以付款人必须改变它们自身的金额状态。
红色箭头是输出。请注意,绿色输入是对之前输出的参考
最后让我们修改我们的wallet类
- 搜集余额(通过循环遍历UTXO列表来检查交易的输出是否是我的)并
- 创建交易
import java.security.*;
import java.security.spec.ECGenParameterSpec;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Wallet {
public PrivateKey privateKey;
public PublicKey publicKey;
public HashMap<String,TransactionOutput> UTXOs = new HashMap<String,TransactionOutput>(); //only UTXOs owned by this wallet.
public Wallet() {...
public void generateKeyPair() {...
//returns balance and stores the UTXO's owned by this wallet in this.UTXOs
public float getBalance() {
float total = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, TransactionOutput> item: NoobChain.UTXOs.entrySet()){
TransactionOutput UTXO = item.getValue();
if(UTXO.isMine(publicKey)) { //if output belongs to me ( if coins belong to me )
UTXOs.put(UTXO.id,UTXO); //add it to our list of unspent transactions.
total += UTXO.value ;
}
}
return total;
}
//Generates and returns a new transaction from this wallet.
public Transaction sendFunds(PublicKey _recipient,float value ) {
if(getBalance() < value) { //gather balance and check funds.
System.out.println("#Not Enough funds to send transaction. Transaction Discarded.");
return null;
}
//create array list of inputs
ArrayList<TransactionInput> inputs = new ArrayList<TransactionInput>();
float total = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, TransactionOutput> item: UTXOs.entrySet()){
TransactionOutput UTXO = item.getValue();
total += UTXO.value;
inputs.add(new TransactionInput(UTXO.id));
if(total > value) break;
}
Transaction newTransaction = new Transaction(publicKey, _recipient , value, inputs);
newTransaction.generateSignature(privateKey);
for(TransactionInput input: inputs){
UTXOs.remove(input.transactionOutputId);
}
return newTransaction;
}
}
你可以随时为钱包添加一些其他功能,例如记录您的交易历史记录。
添加交易到区块中
现在我们已经有了一个有效的交易系统,我们需要把交易加入到我们的区块链中。我们把交易列表替换我们块中无用的数据,但是在一个单一的区块中可能存放了1000个交易,这就会导致大量的hash计算,不用担心在这里我们使用了交易的merkle root,稍后你会看到。让我们增加一个帮助方法来创建merkle root在StringUtils类中。
在StringUtils类中创建getMerkleRoot方法
//Tacks in array of transactions and returns a merkle root.
public static String getMerkleRoot(ArrayList<Transaction> transactions) {
int count = transactions.size();
ArrayList<String> previousTreeLayer = new ArrayList<String>();
for(Transaction transaction : transactions) {
previousTreeLayer.add(transaction.transactionId);
}
ArrayList<String> treeLayer = previousTreeLayer;
while(count > 1) {
treeLayer = new ArrayList<String>();
for(int i=1; i < previousTreeLayer.size(); i++) {
treeLayer.add(applySha256(previousTreeLayer.get(i-1) + previousTreeLayer.get(i)));
}
count = treeLayer.size();
previousTreeLayer = treeLayer;
}
String merkleRoot = (treeLayer.size() == 1) ? treeLayer.get(0) : "";
return merkleRoot;
}
我会尽快用一个实际的merkleroot取代这个方法,但是现在使用这个可以正常运行
修来Block 类
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
public class Block {
public String hash;
public String previousHash;
public String merkleRoot;
public ArrayList<Transaction> transactions = new ArrayList<Transaction>(); //our data will be a simple message.
public long timeStamp; //as number of milliseconds since 1/1/1970.
public int nonce;
//Block Constructor.
public Block(String previousHash ) {
this.previousHash = previousHash;
this.timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
this.hash = calculateHash(); //Making sure we do this after we set the other values.
}
//Calculate new hash based on blocks contents
public String calculateHash() {
String calculatedhash = StringUtil.applySha256(
previousHash +
Long.toString(timeStamp) +
Integer.toString(nonce) +
merkleRoot
);
return calculatedhash;
}
//Increases nonce value until hash target is reached.
public void mineBlock(int difficulty) {
merkleRoot = StringUtil.getMerkleRoot(transactions);
String target = StringUtil.getDificultyString(difficulty); //Create a string with difficulty * "0"
while(!hash.substring( 0, difficulty).equals(target)) {
nonce ++;
hash = calculateHash();
}
System.out.println("Block Mined!!! : " + hash);
}
//Add transactions to this block
public boolean addTransaction(Transaction transaction) {
//process transaction and check if valid, unless block is genesis block then ignore.
if(transaction == null) return false;
if((previousHash != "0")) {
if((transaction.processTransaction() != true)) {
System.out.println("Transaction failed to process. Discarded.");
return false;
}
}
transactions.add(transaction);
System.out.println("Transaction Successfully added to Block");
return true;
}
}
需要注意的是我们还更新了Block构造函数,因为我们不再需要传递字符串数据,并将merkle root包含在计算哈希方法中。addTransaction方法用来增加交易,只有满足条件下才可以成功的在区块中增加交易。
我们已经实现了一个可交易的区块链。
最后的测试
我们应该测试从钱包发送货币,更新区块链并进行有效性检查。但首先我们需要一种将新硬币引入混合的方法。有很多方法来创建新的硬币。在比特币区块链上,有很多方法可以创造新的比特币:矿工可以将交易包括在内,作为对每个矿工挖矿的奖励。但在这里我们只希望在创世纪区块中释放货币。就像比特币中一下,所以我们修改我们的主函数以达到下面的目的。
- 创世纪区块发布100个货币给walletA
- 一个更新的链有效性检查,考虑到交易。
- 测试交易看是否一切正常。
public class NoobChain {
public static ArrayList<Block> blockchain = new ArrayList<Block>();
public static HashMap<String,TransactionOutput> UTXOs = new HashMap<String,TransactionOutput>();
public static int difficulty = 3;
public static float minimumTransaction = 0.1f;
public static Wallet walletA;
public static Wallet walletB;
public static Transaction genesisTransaction;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//add our blocks to the blockchain ArrayList:
Security.addProvider(new org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider()); //Setup Bouncey castle as a Security Provider
//Create wallets:
walletA = new Wallet();
walletB = new Wallet();
Wallet coinbase = new Wallet();
//create genesis transaction, which sends 100 NoobCoin to walletA:
genesisTransaction = new Transaction(coinbase.publicKey, walletA.publicKey, 100f, null);
genesisTransaction.generateSignature(coinbase.privateKey); //manually sign the genesis transaction
genesisTransaction.transactionId = "0"; //manually set the transaction id
genesisTransaction.outputs.add(new TransactionOutput(genesisTransaction.reciepient, genesisTransaction.value, genesisTransaction.transactionId)); //manually add the Transactions Output
UTXOs.put(genesisTransaction.outputs.get(0).id, genesisTransaction.outputs.get(0)); //its important to store our first transaction in the UTXOs list.
System.out.println("Creating and Mining Genesis block... ");
Block genesis = new Block("0");
genesis.addTransaction(genesisTransaction);
addBlock(genesis);
//testing
Block block1 = new Block(genesis.hash);
System.out.println("\nWalletA's balance is: " + walletA.getBalance());
System.out.println("\nWalletA is Attempting to send funds (40) to WalletB...");
block1.addTransaction(walletA.sendFunds(walletB.publicKey, 40f));
addBlock(block1);
System.out.println("\nWalletA's balance is: " + walletA.getBalance());
System.out.println("WalletB's balance is: " + walletB.getBalance());
Block block2 = new Block(block1.hash);
System.out.println("\nWalletA Attempting to send more funds (1000) than it has...");
block2.addTransaction(walletA.sendFunds(walletB.publicKey, 1000f));
addBlock(block2);
System.out.println("\nWalletA's balance is: " + walletA.getBalance());
System.out.println("WalletB's balance is: " + walletB.getBalance());
Block block3 = new Block(block2.hash);
System.out.println("\nWalletB is Attempting to send funds (20) to WalletA...");
block3.addTransaction(walletB.sendFunds( walletA.publicKey, 20));
System.out.println("\nWalletA's balance is: " + walletA.getBalance());
System.out.println("WalletB's balance is: " + walletB.getBalance());
isChainValid();
}
public static Boolean isChainValid() {
Block currentBlock;
Block previousBlock;
String hashTarget = new String(new char[difficulty]).replace('\0', '0');
HashMap<String,TransactionOutput> tempUTXOs = new HashMap<String,TransactionOutput>(); //a temporary working list of unspent transactions at a given block state.
tempUTXOs.put(genesisTransaction.outputs.get(0).id, genesisTransaction.outputs.get(0));
//loop through blockchain to check hashes:
for(int i=1; i < blockchain.size(); i++) {
currentBlock = blockchain.get(i);
previousBlock = blockchain.get(i-1);
//compare registered hash and calculated hash:
if(!currentBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.calculateHash()) ){
System.out.println("#Current Hashes not equal");
return false;
}
//compare previous hash and registered previous hash
if(!previousBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.previousHash) ) {
System.out.println("#Previous Hashes not equal");
return false;
}
//check if hash is solved
if(!currentBlock.hash.substring( 0, difficulty).equals(hashTarget)) {
System.out.println("#This block hasn't been mined");
return false;
}
//loop thru blockchains transactions:
TransactionOutput tempOutput;
for(int t=0; t <currentBlock.transactions.size(); t++) {
Transaction currentTransaction = currentBlock.transactions.get(t);
if(!currentTransaction.verifiySignature()) {
System.out.println("#Signature on Transaction(" + t + ") is Invalid");
return false;
}
if(currentTransaction.getInputsValue() != currentTransaction.getOutputsValue()) {
System.out.println("#Inputs are note equal to outputs on Transaction(" + t + ")");
return false;
}
for(TransactionInput input: currentTransaction.inputs) {
tempOutput = tempUTXOs.get(input.transactionOutputId);
if(tempOutput == null) {
System.out.println("#Referenced input on Transaction(" + t + ") is Missing");
return false;
}
if(input.UTXO.value != tempOutput.value) {
System.out.println("#Referenced input Transaction(" + t + ") value is Invalid");
return false;
}
tempUTXOs.remove(input.transactionOutputId);
}
for(TransactionOutput output: currentTransaction.outputs) {
tempUTXOs.put(output.id, output);
}
if( currentTransaction.outputs.get(0).reciepient != currentTransaction.reciepient) {
System.out.println("#Transaction(" + t + ") output reciepient is not who it should be");
return false;
}
if( currentTransaction.outputs.get(1).reciepient != currentTransaction.sender) {
System.out.println("#Transaction(" + t + ") output 'change' is not sender.");
return false;
}
}
}
System.out.println("Blockchain is valid");
return true;
}
public static void addBlock(Block newBlock) {
newBlock.mineBlock(difficulty);
blockchain.add(newBlock);
}
}
打印:
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:57085', transport: 'socket'
Creating and Mining Genesis block...
Transaction Successfully added to Block
Block Mined!!! : 000b5a7ca6bf07639122cb31e884996895a482c281dd89c203824f1e93a661bf
WalletA's balance is: 100.0
WalletA is Attempting to send funds (40) to WalletB...
Transaction Successfully added to Block
Block Mined!!! : 000c7f814357abfea86ad1b38ec1dc3afed2afc9107f2bacc933d8136bf34df0
WalletA's balance is: 60.0
WalletB's balance is: 40.0
WalletA Attempting to send more funds (1000) than it has...
#Not Enough funds to send transaction. Transaction Discarded.
Block Mined!!! : 000b3822fb7985db438712816727d4bc382926a1c4654062aad4071d9b9fad98
WalletA's balance is: 60.0
WalletB's balance is: 40.0
WalletB is Attempting to send funds (20) to WalletA...
Transaction Successfully added to Block
WalletA's balance is: 80.0
WalletB's balance is: 20.0
Blockchain is valid
现在钱包能够安全地在您的区块链上发送金额,只要他们有金额发送。这意味着你有你自己的本地加密货币
可以进行交易的区块链
你已经成功地创建了自己的加密货币。你的区块链:
- 允许用户创建钱包
- 使用椭圆曲线加密方式为钱包提供公钥和私钥
- 通过使用数字签名算法证明所有权,确保资金转移
- 允许用户在区块链上进行交易
原文链接:Creating Your First Blockchain with Java. Part 2-Transactions
代码下载
从我的 github 中下载,https://github.com/longfeizheng/blockchain-java
🙂🙂🙂关注微信小程序java架构师历程 上下班的路上无聊吗?还在看小说、新闻吗?不知道怎样提高自己的技术吗?来吧这里有你需要的java架构文章,1.5w+的java工程师都在看,你还在等什么?