重叠泪痕缄锦字,人生只有情难死。
概述
本文将了解资源或文件(例如文本文件、XML文件、属性文件或图像文件)加载到Spring应用程序上下文中的不同实现。Spring ResourceLoader为我们提供了一个统一的getResource()方法来通过资源路径检索外部资源。
资源(Resource)接口
Resource是Spring中用于表示外部资源的通用接口。
Spring为Resource接口提供了以下6种实现。
UrlResourceClassPathResourceFileSystemResourceServletContextResourceInputStreamResourceByteArrayResource
我们可以指定不同的前缀来创建路径以从不同位置加载资源
| 前缀 | 示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
classpath: |
classpath:com/myapp/config.xml |
从类路径加载 |
file: |
file:///data/config.xml |
从文件系统作为URL加载。 |
http: |
https://myserver/logo.png |
从URL加载 |
(none) |
/data/config.xml |
取决于底层的ApplicationContext |
ResourceLoader
它用于加载资源(例如类路径或文件系统资源)。它有两种方法:
//Expose the ClassLoader used by this ResourceLoader.
ClassLoader getClassLoader()
//Return a Resource handle for the specified resource location.
Resource getResource(String location)
getResource()方法将根据资源路径决定要实例化的Resource实现。
要获取ResourceLoader的引用,请实现ResourceLoaderAware接口。
Resource banner = resourceLoader.getResource("file:c:/temp/filesystemdata.txt");
使用ApplicationContext加载资源
在Spring中,所有应用程序上下文都实现ResourceLoader接口。因此,所有应用程序上下文都可用于获取资源实例。
要获取ApplicationContext的引用,请实现ApplicationContextAware接口。
Resource banner = ctx.getResource("file:c:/temp/filesystemdata.txt");
使用ResourceLoaderAware加载资源
为了演示下面的各种示例,我将一个具有相同名称的文件放置在不同的位置,并且我将演示如何加载每个文件。
CustomResourceLoader.java的编写如下,它将已加载的资源文件的内容打印到控制台中。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
public class CustomResourceLoader implements ResourceLoaderAware
{
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
public void showResourceData() throws IOException
{
//This line will be changed for all versions of other examples
Resource banner = resourceLoader.getResource("file:c:/temp/filesystemdata.txt");
InputStream in = banner.getInputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
while (true) {
String line = reader.readLine();
if (line == null)
break;
System.out.println(line);
}
reader.close();
}
}
该文件的applicationContext.xml文件条目如下:
<bean id="customResourceLoader" class="cn.howtodoinjava.demo.CustomResourceLoader"></bean>
为了测试CustomResourceLoader bean并调用showResourceData()方法,使用了以下代码:
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CustomResourceLoader customResourceLoader = (CustomResourceLoader) context.getBean("customResourceLoader");
customResourceLoader.showResourceData();
}
由于我们正在通过
Spring的资源加载器访问资源,因此自定义资源加载器必须实现ApplicationContextAware接口或ResourceLoaderAware接口。
加载外部资源
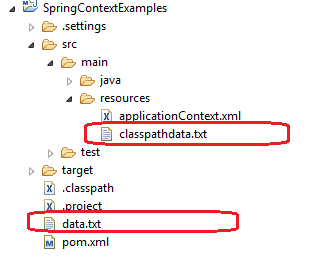
从应用程序根文件夹加载资源
要从应用程序文件夹加载文件,请使用以下模板:
Resource banner = resourceLoader.getResource("file:data.txt");
从类路径加载资源
要从类路径加载文件,请使用以下模板:
Resource banner = resourceLoader.getResource("classpath:classpathdata.txt");
从文件系统加载资源
要从应用程序文件夹外部的文件系统加载文件,请使用以下模板:
Resource banner = resourceLoader.getResource("file:c:/temp/filesystemdata.txt");
从URL加载资源
要从任何URL加载文件,请使用以下模板:
Resource banner = resourceLoader.getResource("//howtodoinjava.com/readme.txt");
以上所有示例将从其位置加载资源文件,你可以按需要使用它们。
如何注入外部文件
在上面的示例中,我们在CustomResourceLoader中对资源名称进行了硬编码,很多人可能不喜欢它,并且希望通过上下文文件对其进行配置。使用下面的代码模板可以配置外部资源名称。
<bean id="customResourceLoader" class="com.howtodoinjava.demo.CustomResourceLoader">
<property name="resource">
<value>classpath:classpathdata.txt</value>
<!-- or -->
<value>file:data.txt</value>
</property>
</bean>
CustomResourceLoader如下所示:
public class CustomResourceLoader {
private Resource resource;
public Resource getResource() {
return resource;
}
public void setResource(Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
}
在上下文初始化后,资源将注入到CustomResourceLoader的resource属性中。在Spring Boot Resourceloader示例中也可以使用相同的代码。
🙂🙂🙂关注微信公众号java干货 不定期分享干货资料